💉 External Ventricular Drain (EVD) – Key Points
Definition:
A temporary catheter placed into the lateral ventricle to drain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 💧 or monitor intracranial pressure (ICP 📊).
🔹 Placement Site & Technique 🏥
1️⃣ Typical Entry:
- Through a burr hole in the frontal region 🧠
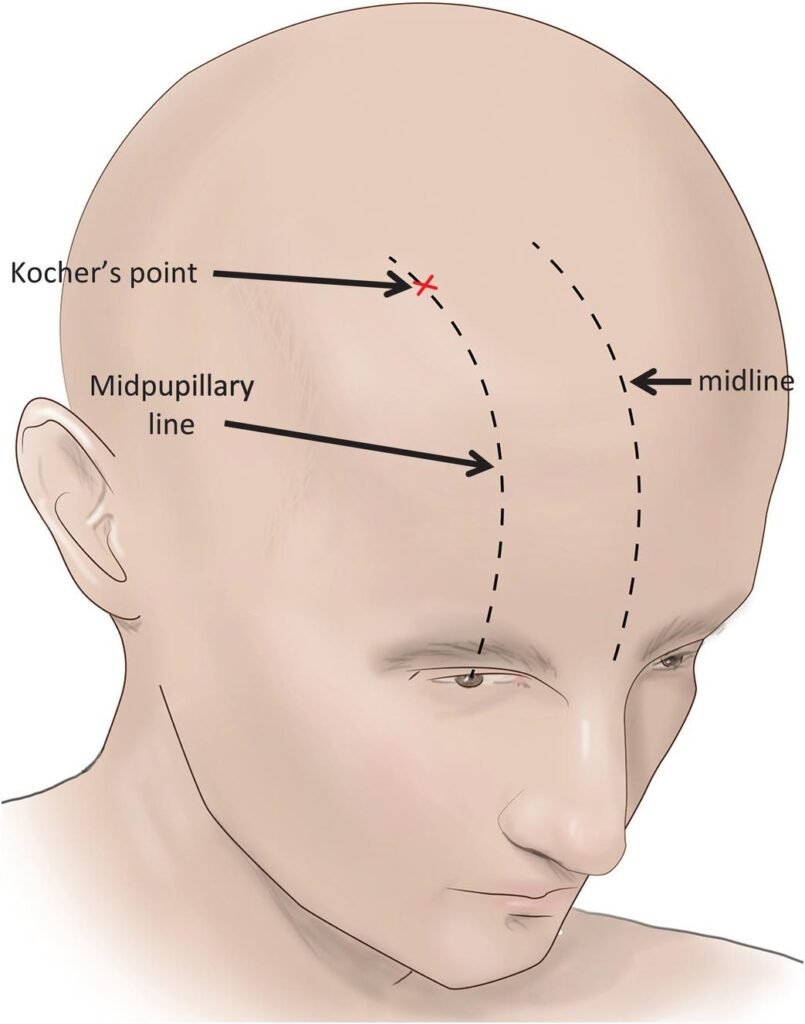
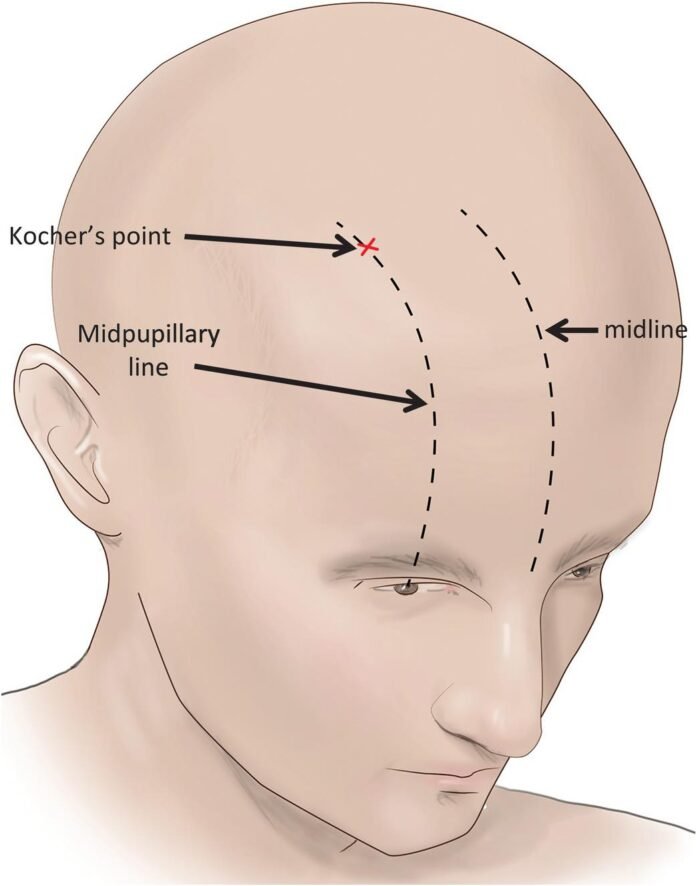
- Most common anatomical point: Kocher’s Point 📍
2️⃣ Kocher’s Point Location:
- ~2–3 cm lateral to midline ↔
- ~11 cm posterior to nasion 🦴
- Anterior to coronal suture
3️⃣ Why Frontal Placement?
- Direct access to frontal horn of lateral ventricle 🧠
- Minimizes risk to eloquent cortex ⚡
- Easier to secure and maintain 🔧
🔹 Summary of Procedure ✨
- Burr hole 🛠️ created at Kocher’s point
- Catheter advancement ➡️ into lateral ventricle
- Used for:
- CSF drainage 💧
- ICP monitoring 📊
💡 Clinical Pearls
- Usually done at bedside or OR 🏥
- Requires neurosurgeon or trained neurocritical care team 👨⚕️👩⚕️
- Correct placement confirmed by CT scan 🖥️ or ventricular CSF flow