🧠🧬 Pathogenesis of Neurodegeneration – High-Yield Overview
Definition:
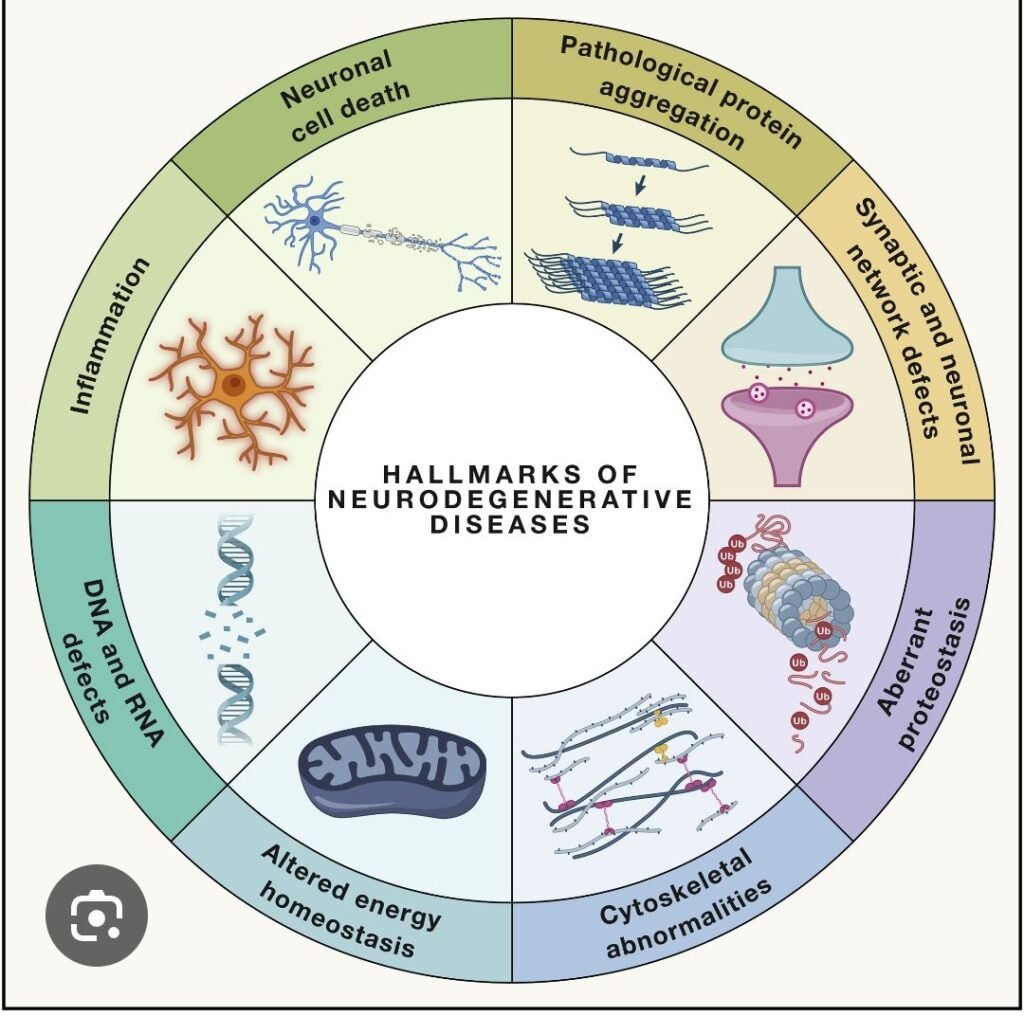
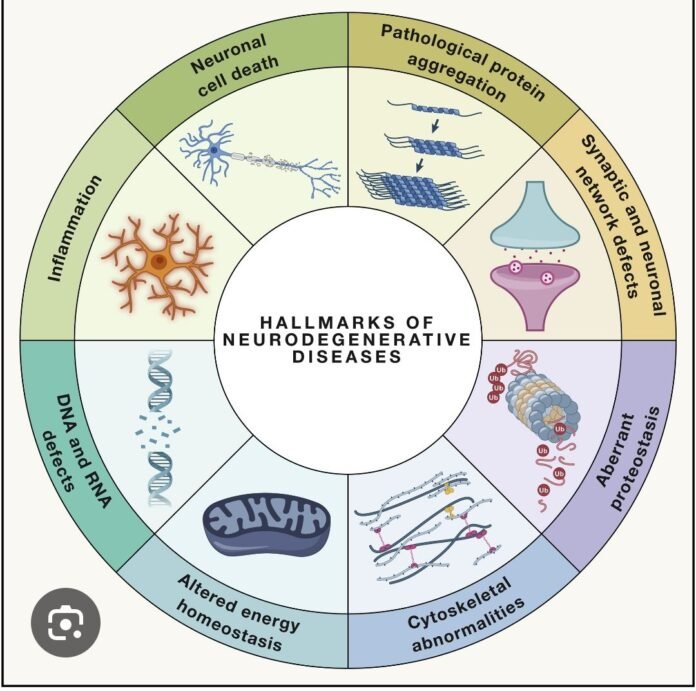
Progressive dysfunction and death of neurons due to interacting molecular pathways, leading to cognitive, motor, or behavioral deficits. Despite different clinical phenotypes, most neurodegenerative diseases share common mechanisms.
🔹 1️⃣ Protein Misfolding & Aggregation (Proteostasis Failure)
- Misfolded proteins → oligomers → accumulation → overwhelm clearance systems
- Clearance failure: ubiquitin–proteasome system, autophagy–lysosome pathway
- Disease examples:
- 🧠 Alzheimer’s: Aβ plaques, tau tangles
- 🟣 Parkinson’s: α-synuclein (Lewy bodies)
- 🧩 ALS/FTD: TDP-43, FUS
- 🟡 Huntington’s: mutant huntingtin (polyQ repeats)
- Toxic effects: synaptic disruption, ER stress, apoptosis, prion-like spread
🔹 2️⃣ Mitochondrial Dysfunction
- ↓ ATP → synaptic failure
- ↑ Reactive oxygen species (ROS)
- Fission–fusion imbalance
- Release of pro-apoptotic factors
- Diseases: Parkinson’s (complex I, PINK1/parkin), ALS, Alzheimer’s, mitochondrial encephalopathies
🔹 3️⃣ Oxidative Stress & Free Radical Injury
- ROS damage DNA, proteins, lipids
- Sources: mitochondria, microglia, iron accumulation, environmental toxins
- Consequences: lipid peroxidation, DNA damage, protein oxidation → misfolding
🔹 4️⃣ Excitotoxicity (Glutamate-Mediated)
- Excess NMDA/AMPA receptor activation → ↑ intracellular Ca²⁺
- Mitochondrial failure, ROS, calpain activation → cytoskeletal breakdown
- Diseases: ALS, Huntington’s, acute insults (stroke, hypoxia)
🔹 5️⃣ Impaired Axonal Transport
- Microtubules & motor proteins (kinesin/dynein) fail
- Consequences: synaptic starvation, toxic cargo accumulation, “dying-back” neuropathy
- Examples: ALS (TDP-43), Tauopathies
🔹 6️⃣ Neuroinflammation (Glial-Mediated)
- Chronic microglia & astrocyte activation → IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, complement activation
- Reactive astrocytes (A1 phenotype) become neurotoxic
- Diseases: Alzheimer’s (TREM2 risk), Parkinson’s, ALS
🔹 7️⃣ Synaptic Dysfunction
- Early mechanism preceding neuronal death
- Mechanisms:
- Aβ oligomers block NMDA/AMPA signaling
- α-synuclein disrupts vesicle release
- Prion-like spreading disrupts networks
- Clinical implication: early cognitive/motor changes before structural atrophy
🔹 8️⃣ Genetic Vulnerability
- Mutations disrupt cellular pathways:
- APP, PSEN1/2 → early-onset Alzheimer’s
- LRRK2, PARKIN, PINK1, GBA → Parkinson’s
- C9orf72 → ALS/FTD
- HTT expansion → Huntington’s
- Mechanisms: gain of toxic function or loss of normal function
🔹 9️⃣ Impaired Autophagy–Lysosome Pathway
- Defective autophagosome formation, lysosomal enzyme deficiency, impaired mitophagy
- Diseases: Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, lysosomal storage disorders, C9orf72 ALS
🔹 🔟 Prion-like Propagation
- Misfolded proteins template misfolding in neighboring cells
- Agents: Aβ, tau, α-synuclein, huntingtin, TDP-43
- Explains progressive spread (e.g., Braak staging in AD/Parkinson’s)
🔹 Integrated Model
- Misfolded proteins accumulate
- Mitochondrial failure → energy crisis
- Axonal transport collapses
- Synapses weaken → cognitive/motor deficits
- Chronic inflammation accelerates death
- Neurons undergo apoptosis/necrosis
💡 High-Yield Clinical Pearls
- Neurodegeneration begins with synaptic dysfunction, not cell death
- Protein aggregation + impaired autophagy = central mechanism
- Mitochondria & microglia = key therapeutic targets
- Prion-like spread explains topographical progression
- Genetics → pathway; environment → disease rate