🧠🔬 McDonald Criteria 2024 – High-Yield Summary
Definition:
MS diagnosis requires Dissemination in Space (DIS) 🌐) and Dissemination in Time (DIT ⏳), plus exclusion of alternative diagnoses.
🔹 Key Updates in 2024 Revision
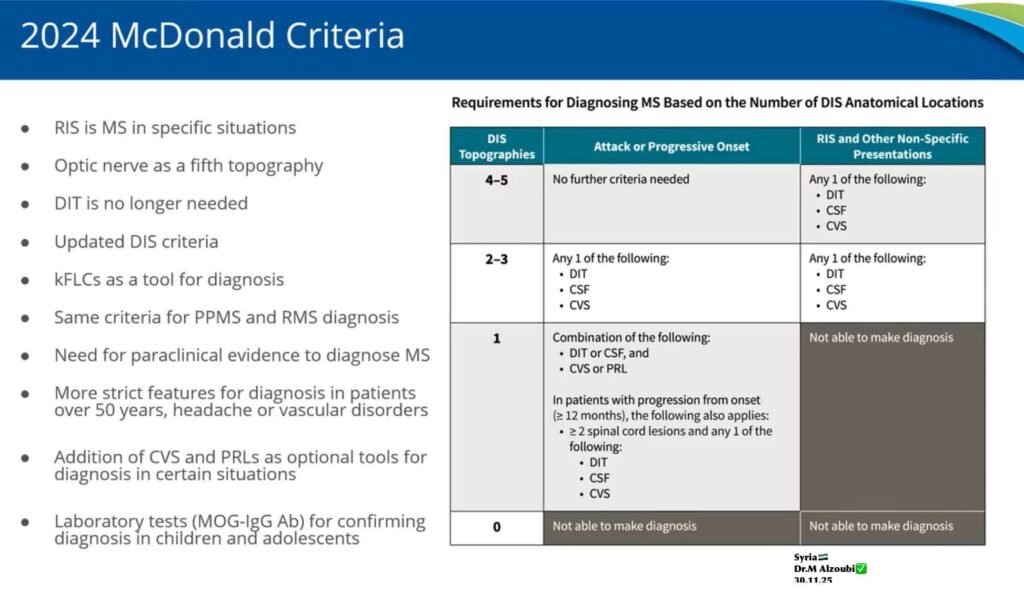
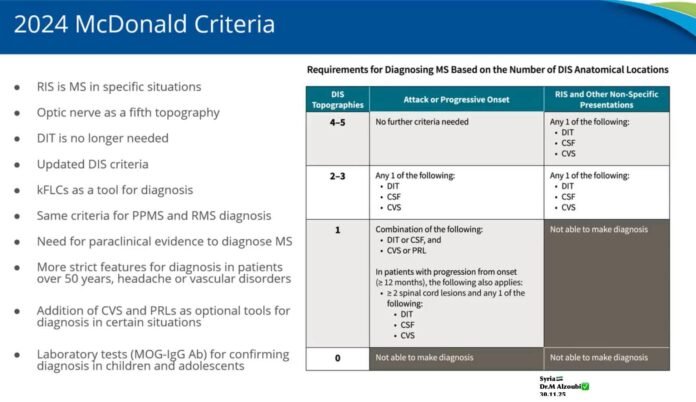
1️⃣ Dissemination in Space (DIS) 🌐
- Lesions must involve ≥1 of 5 CNS regions:
- 🧩 Periventricular
- 🧠 Juxtacortical / Cortical
- 🏰 Infratentorial
- 🦴 Spinal cord
- 👁️ Optic nerve ✅ (new inclusion)
2️⃣ Dissemination in Time (DIT) ⏳
- Not strictly required in some cases
- Single clinical event or radiologically isolated cases may suffice with supporting evidence
3️⃣ New Biomarkers 🧬
- Kappa Free-Light Chain (kFLC) index in CSF ✅ (alternative to oligoclonal bands)
- Detects intrathecal antibody production 🧪
4️⃣ Advanced MRI Features 🖥️🧲
- Central Vein Sign (CVS) 💉
- Paramagnetic Rim Lesions (PRL) 🔵
- Helps differentiate MS lesions from vascular/migraine lesions
5️⃣ Flexibility for Special Populations 👶🧓
- Radiologically Isolated Syndrome (RIS) 📸: MRI lesions + biomarkers may allow early diagnosis
- Pediatric-onset MS 👦👧: Consider MOG-antibody testing in atypical events
- Older adults ≥50 🧓: Require robust evidence (spinal lesions, CSF/kFLC+, or multiple CVS+ lesions)
⚡ Strengths / Advantages ✅
- Earlier diagnosis ⏱️ → prompt treatment, relapse prevention
- More sensitive & flexible 🔬 — includes optic nerve involvement, isolated MRI lesions
- New biomarkers 🧪 improve specificity → reduce misdiagnosis
⚠️ Limitations / Cautions ⚠️
- Older adults / vascular comorbidities → require stronger evidence
- CVS/PRL need high-quality MRI sequences 🖥️ — may not be available everywhere
- Diagnosis = one of exclusion ❌ (rule out infection 🦠, vascular 🫀, metabolic ⚗️, MOG-associated disorders)
📝 Practical Tips for Resource-Limited Settings 💡
- Use kFLC index 🧬 if OCB testing unavailable
- Optic MRI 👁️, VEP ⚡, OCT 🔬 for optic neuritis
- Interpret advanced MRI signs carefully if specialized sequences not available