⚡ Epileptogenesis – High-Yield Overview
Definition:
Biological process by which a normal brain becomes capable of spontaneous, recurrent seizures. Involves molecular, cellular, and network-level changes over time.
🔹 1️⃣ Latent Period After Insult
- Occurs after:
- 💥 Traumatic brain injury
- 🧩 Stroke
- 🦠 CNS infections
- ⚡ Status epilepticus
- 🧬 Genetic predisposition
- 🧠 Neurodegenerative disease
- Latent period: days → months → years
- Silent phase: nervous system “rewires” into hyperexcitable networks
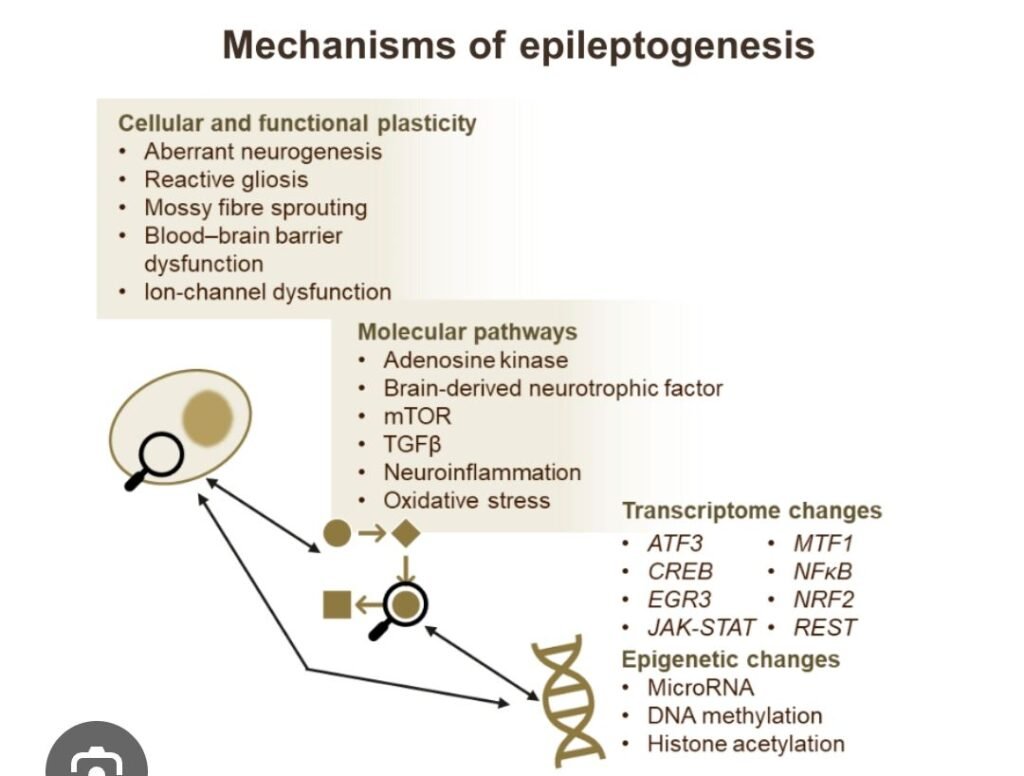
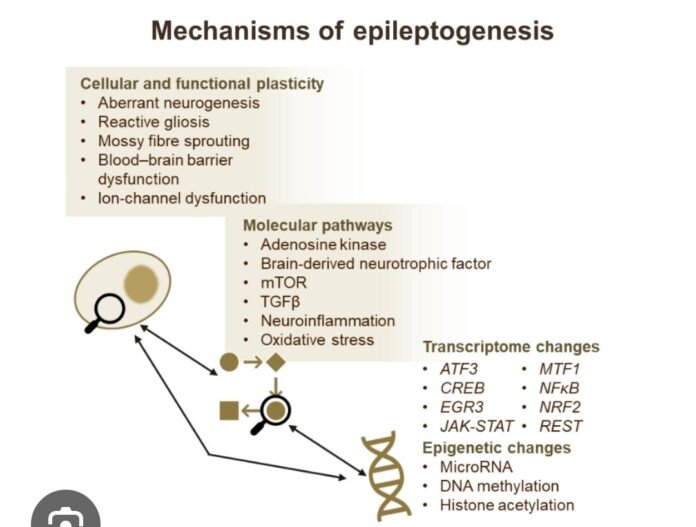
🔹 2️⃣ Core Mechanisms
A. Neuronal Hyperexcitability
- ↑ Glutamatergic transmission (NMDA/AMPA)
- ↓ GABAergic inhibition (loss of interneurons, receptor changes)
- ↑ Intrinsic excitability:
- ↑ Na⁺ channel activity
- ↓ K⁺ conductance
- HCN channel downregulation
B. Synaptic Reorganization
- 🌱 Mossy fiber sprouting (dentate granule cells → recurrent excitatory loops)
- Axonal sprouting → new excitatory circuits
- Loss of inhibitory network re-establishment
C. Structural Remodeling
- 🧠 Hippocampal sclerosis (CA1, CA3, hilus)
- Gliosis (astrocytes, microglia)
- Dendritic spine loss/abnormal growth → hypersynchronous discharge
D. Neuroinflammation
- Activation of microglia & astrocytes
- Cytokines: IL-1β, TNF-α
- Complement cascade
- Consequences: ↑ glutamate, ↓ GABA, BBB disruption
E. Blood–Brain Barrier Breakdown
- Albumin entry → TGF-β signaling
- Potassium buffering failure
- ↑ Extracellular glutamate → hyperexcitability
F. Epigenetic & Genetic Modifications
- DNA methylation changes
- miRNA dysregulation
- Long-term channel/synaptic protein alterations
G. Network-Level Changes
- Loss of parvalbumin-positive interneurons
- Abnormal gap junction synchronization (connexin 36)
- Thalamocortical oscillation instability
- Self-sustaining seizure networks
🔹 3️⃣ Stages of Epileptogenesis
- Initiation Stage: acute excitotoxicity & ionic shifts
- Latent Phase: silent period, synaptic remodeling, neuroinflammation, gliosis, channel alterations
- Chronic Epileptic Stage: recurrent unprovoked seizures from hyperexcitable networks
🔹 4️⃣ Clinical Examples
- Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: mossy fiber sprouting, hippocampal sclerosis
- Post-traumatic Epilepsy: BBB breakdown, microglial activation, network reorganization
- Post-stroke Epilepsy: excitotoxicity, gliotic scar hyperexcitability
- Genetic Epilepsies: channelopathies (SCN1A, KCNQ2) → pre-epileptic circuits
🔹 5️⃣ Antiepileptogenic Therapy Targets (Experimental)
- Anti-inflammatory agents (IL-1β blockers, COX-2 inhibitors)
- mTOR inhibitors (tuberous sclerosis)
- Sodium channel blockers to prevent network synchronization
- Inhibition of mossy fiber sprouting
- Modulation of GABAergic networks
- Block albumin–TGF-β signaling after BBB disruption
- ⚠️ No approved antiepileptogenic drug exists in humans yet
🔹 6️⃣ Clinical Pearls
- Early post-stroke/TBI seizures ≠ future epilepsy
- Severity of injury, imaging, EEG abnormalities predict risk
- Normal MRI does not exclude epileptogenesis (channelopathies/microcircuits matter)
- EEG high-frequency oscillations (HFOs) = emerging biomarker
- Longer latent period = wider window for intervention