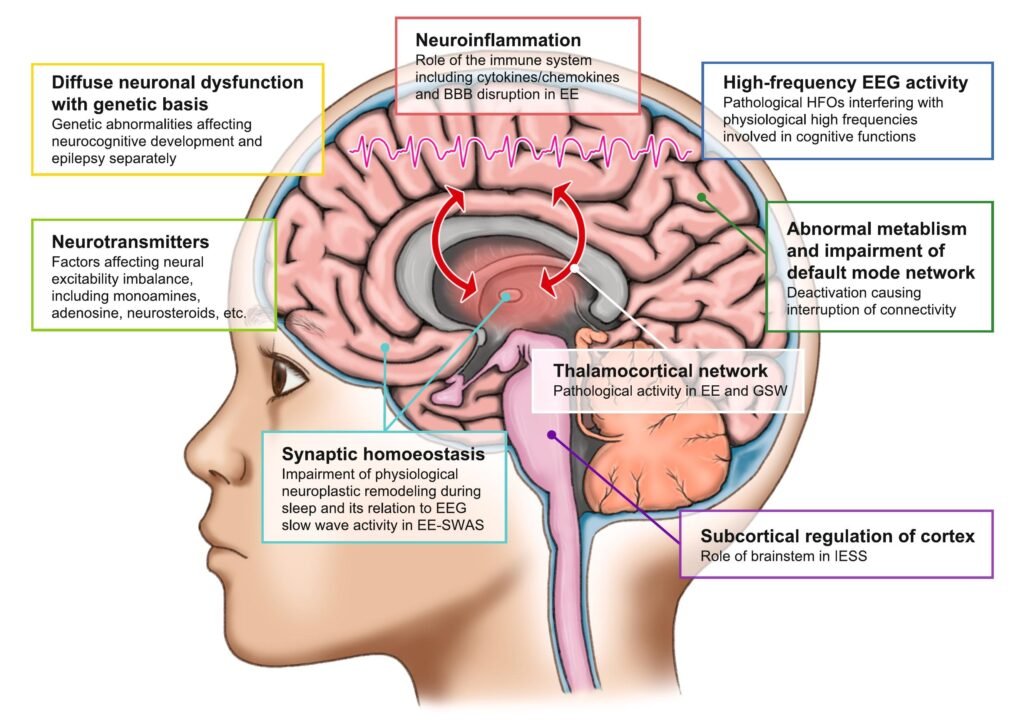
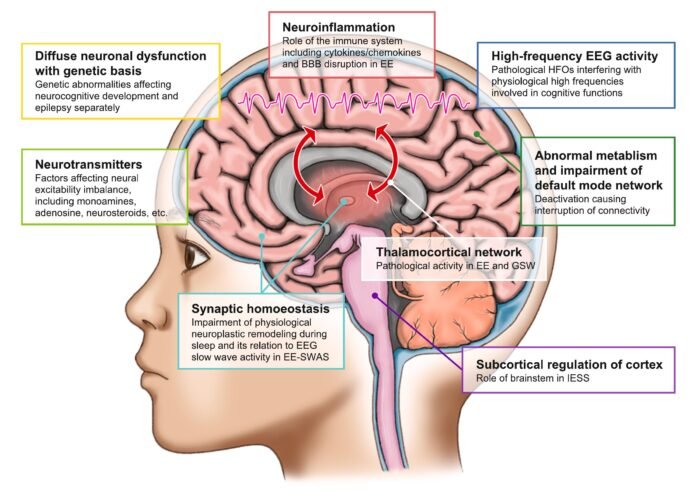
Definition
- A group of severe childhood epilepsies where epileptic activity itself causes progressive cognitive, behavioral, or developmental decline
- Seizures + EEG abnormalities are toxic to the brain
⭐ Core Features
- 👶 Early onset (infancy/early childhood)
- ⚡ Frequent, severe, drug-resistant seizures
- 📈 Abundant interictal discharges
- 🧠 Developmental delay/regression
- 📉 Abnormal background EEG
- 🎗️ High risk of long-term neurocognitive disability
🍼 1. Ohtahara Syndrome (Early Infantile EE)
- ⏳ Neonatal onset
- ⚡ Tonic spasms, frequent
- 📉 EEG: Burst–suppression
- 🔄 Evolves to West syndrome
Treatment
- 💉 High-dose steroids
- 💊 Vigabatrin (TS)
- 🍽️ Ketogenic diet
- Levetiracetam, topiramate
- 🔪 Surgery (focal dysplasia)
👶 2. West Syndrome (Infantile Spasms)
Triad
- ⚡ Epileptic spasms
- 🧠 Developmental regression
- 📉 Hypsarrhythmia
Onset: 3–12 months
Treatment
- ⭐ ACTH / high-dose prednisolone
- 💊 Vigabatrin (TS)
- 🍽️ Ketogenic diet
- Levetiracetam, topiramate
- 🧪 Treat metabolic causes (B6, PLP, biotin)
🧩 3. Lennox–Gastaut Syndrome (LGS)
- ⏳ Onset: 1–8 years
- ⚡ Seizures: atonic, atypical absences, tonic, myoclonic
- 📉 EEG:
- <3 Hz slow spike-wave
- Paroxysmal fast activity in sleep
Treatment
- Valproate
- Clobazam
- Lamotrigine
- Rufinamide
- Topiramate
- 🍽️ Ketogenic diet
- 🔌 VNS
- ✂️ Corpus callosotomy
🔥 4. Dravet Syndrome
- 🧬 SCN1A mutation
- Onset after prolonged febrile seizure
- Fever-sensitive, drug-resistant
❌ Avoid sodium channel blockers:
CBZ, LTG, PHT
Treatment
- Valproate
- Clobazam
- Topiramate
- Stiripentol
- Cannabidiol
- Fenfluramine
- 🍽️ Ketogenic diet
🌙 5. Doose Syndrome (Myoclonic–Astatic Epilepsy)
- Onset 2–6 years
- Myoclonic, atonic, absence seizures
- EEG: 2–3 Hz spike-wave
Treatment
- Valproate
- ⭐ Ketogenic diet (most effective)
- Levetiracetam
- Clobazam
🌙 6. CSWS / ESES
- ⭐ Spike-wave index >85% during sleep
- Language regression, cognitive decline
- Onset 2–8 years
Treatment
- High-dose steroids / IVMP
- Clobazam, diazepam
- Valproate
- Levetiracetam
- Sulthiame
- 🔪 Surgery if focal lesion
🗣️ 7. Landau–Kleffner Syndrome (LKS)
- 🎧 Acquired aphasia + auditory agnosia
- Abnormal EEG during sleep
Treatment
- Steroids
- Benzodiazepines
- Valproate
- Speech therapy
- Subpial transections (refractory)
🧬 8. Metabolic / Pyridoxine-Dependent EE
- Neonatal refractory seizures
- Consider metabolic causes
Workup / Treatment
- Pyridoxine (B6) trial
- Pyridoxal phosphate
- Folinic acid
- Biotin (biotinidase deficiency)
💡 High-Yield Treatment Principles
- ⚡ Treat early to prevent developmental harm
- 🔬 Evaluate metabolic and genetic causes
- ⭐ ACTH/steroids for spasms
- 🍽️ Ketogenic diet for drug-resistant EE
- 🔪 Surgery for focal structural lesions
- ❌ Avoid sodium channel blockers in SCN1A disorders