🌩️ Pathophysiology of Migraine (High-Performance Summary)
Migraine = a complex neurovascular network disorder driven by brain hyperexcitability, trigeminovascular activation, and defective pain modulation.
❄️1. Genetic & Neural Hyperexcitability
- ✔️ Migraine brains show increased cortical excitability, especially in the occipital cortex.
- ✔️ Mutations affecting ion channels, glutamate signaling, & inhibitory circuits lower the firing threshold.
- ✔️ FHM gene mutations:
- CACNA1A, ATP1A2, SCN1A → ↑ glutamate, impaired neuronal homeostasis.
- ✔️ Clinical pearl: Hyperexcitability explains sensitivity to light, stress, hormones, sleep loss and why visual aura starts in the occipital cortex.
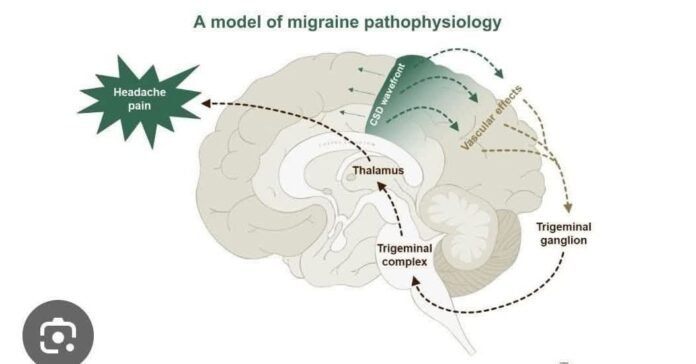
❄️2. Cortical Spreading Depression (CSD) → Aura
- ✔️ A slow depolarization wave moves across cortex at ~3 mm/min.
- CSD produces aura depending on the region it crosses:
- 👁️ Occipital cortex → visual aura
- ✋ Parietal cortex → sensory aura
- 🗣️ Temporal cortex → language/aphasic aura
- ✔️ CSD also activates trigeminovascular pathways, causing headache—even without visible aura (subclinical CSD).
❄️3. Trigeminovascular Activation (Core Pain Generator)
- ✔️ Brainstem dysfunction triggers trigeminal nerve activation.
- ✔️ Release of CGRP, Substance P, Neurokinin A →
- 🩸 Meningeal vasodilation
- 🔥 Neurogenic inflammation
- 📈 Peripheral sensitization → throbbing, movement-worsened pain
- ✔️ CGRP is the dominant pathway, explaining the efficacy of:
- Anti-CGRP monoclonal antibodies
- CGRP receptor antagonists (gepants)
❄️4. Central Sensitization (Pain Becomes Diffuse & Persistent)
- ✔️ Continued attack → hyperactivity in trigeminal nucleus caudalis.
- Leads to:
- Spread of pain
- Persistence of symptoms
- Allodynia: pain from brushing hair, touching face
- ✔️ Explains:
- Why late triptan use is less effective
- How episodic migraine becomes chronic
❄️5. Brainstem Dysfunction
Functional imaging shows abnormal activation in:
- 🧠 Dorsal pons
- 🎯 Periaqueductal gray (PAG)
- 🔵 Locus coeruleus
These regulate:
- 🔽 Descending pain inhibition
- 🤢 Nausea/vomiting
- 🌡️ Autonomic symptoms
- 🌞 Photophobia & phonophobia
Prodrome features: yawning, food cravings, fatigue → explained by brainstem dysregulation.
❄️6. Vascular Mechanisms (Now Secondary)
- Old theory: migraine = primary vasodilation (❌ outdated).
- Current view: vascular changes are consequences, not the root cause.
- Still relevant because:
- CGRP → vasodilation → throbbing pain
- Triptans → cranial vasoconstriction + ↓ presynaptic CGRP release
❄️7. Hormonal Influences
- Estrogen fluctuations: ↑ glutamate, ↓ GABA → lower migraine threshold.
- Explains:
- Menstrual migraines
- Perimenopausal worsening
❄️8. Inflammation & Immune System
- Meningeal cells release histamine and prostaglandins.
- Microglial activation contributes to chronic migraine.
- Connects migraine with co-morbidities:
- IBS
- Fibromyalgia
- Anxiety & depression
❄️ High-Performance Clinical Recap
Migraines are driven by:
- Genetic cortical hyperexcitability
- Cortical spreading depression → aura
- Trigeminovascular activation → CGRP release → inflammation
- Brainstem dysfunction → pain modulation failure + autonomic symptoms
- Central sensitization → chronic migraine + allodynia
- Hormonal & immune factors lowering threshold