🧠🦴 Cauda Equina Syndrome (CES)
Definition:
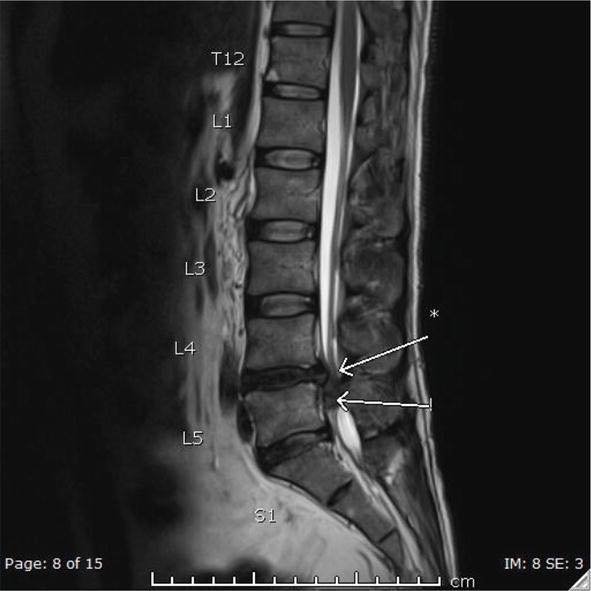
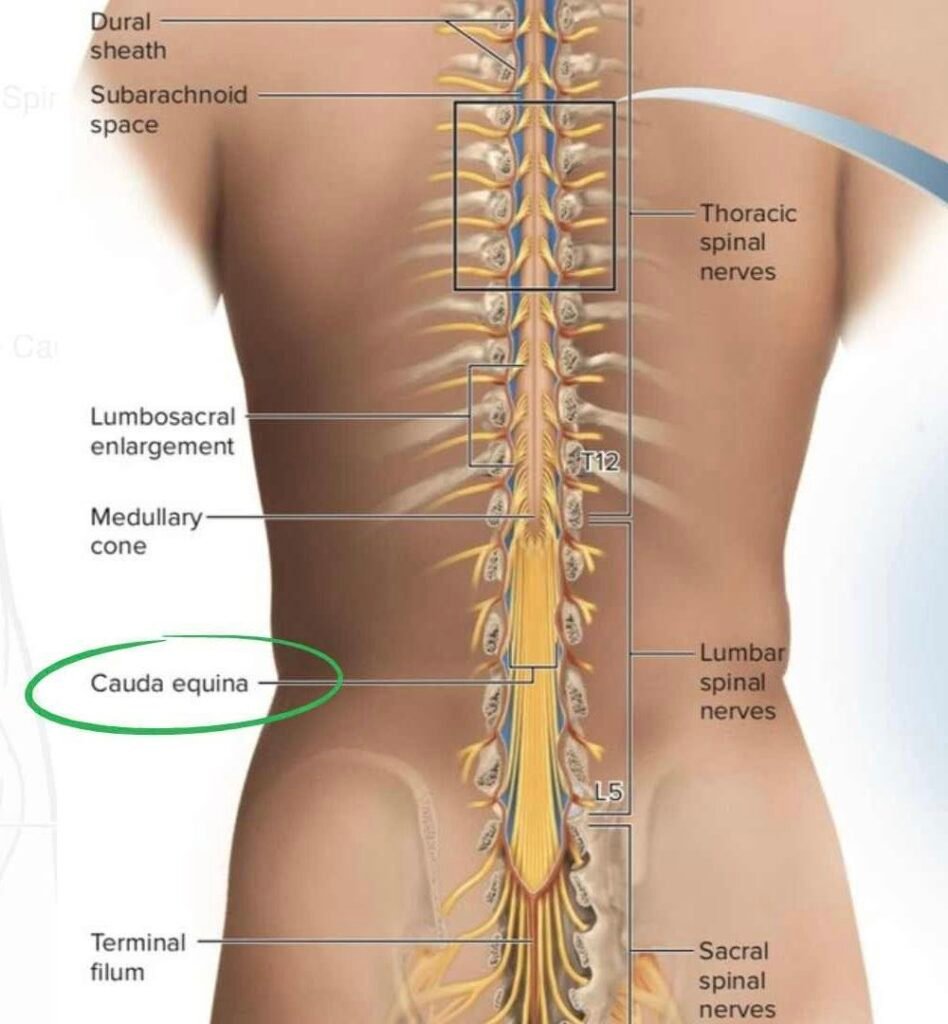
Severe compression of lumbosacral nerve roots (L2–S5) → motor weakness, sensory loss, bladder/bowel dysfunction. Neurosurgical emergency; delayed treatment may cause permanent disability.
📍 Causes / Pathophysiology
- ⚡ Compression of cauda equina nerve roots within lumbar canal
- 💢 Most common: massive central lumbar disc herniation (L4–L5, L5–S1)
- 🧩 Other causes:
- Spinal stenosis
- Epidural abscess
- Epidural hematoma
- Tumors (metastatic / primary)
- Trauma / burst fractures
- 🧠 Effect: sensory, motor, autonomic fibers compressed → saddle anesthesia, sphincter dysfunction, lower-limb weakness
⌛ Epidemiology
- Rare: 1–3 / 100,000 per year
- Adults 30–50 years most affected
- High risk with large disc herniation (esp. L4–L5)
- Diagnostic delay → major medico-legal risk
📈 Clinical Features (Red-Flag Symptoms)
- 🔴 Severe Low Back Pain → sudden, radiates bilaterally (sciatica)
- 🔴 Saddle Anesthesia → numbness in perineum, buttocks, inner thighs (S2–S5 dermatomes)
- 🔴 Bladder Dysfunction
- Urinary retention (most reliable sign)
- Overflow incontinence (late)
- 🔴 Bowel Dysfunction
- Reduced anal tone
- Fecal incontinence (late)
- 🔴 Lower Limb Neurologic Deficits
- Bilateral weakness
- Decreased reflexes (knee, ankle)
- Sexual dysfunction
⚠️ Subtypes:
- CES-Incomplete (CES-I) → sensory loss, still able to void
- CES-Retention (CES-R) → painless urinary retention, high risk of permanent damage
📚 Investigations / Diagnosis
- 🧲 MRI Lumbar Spine → Gold Standard; urgent (hours, not days)
- 💧 Post-void residual bladder scan → >200 mL = retention
- 🧠 Neurological exam → perineal sensation, anal tone, bulbocavernosus reflex, lower extremity strength/reflexes
- 🧪 Labs if infection suspected → CBC, CRP, ESR, blood cultures (epidural abscess)
🚨 Clinical Importance
- Surgical emergency → irreversible nerve damage can occur within 6–12 hours
- Delay → permanent urinary retention, sexual dysfunction, chronic neuropathic pain, lower limb weakness
- Major medico-legal concern in emergency medicine
💊 Treatment / Management
1️⃣ Immediate ED Actions
- Treat pain aggressively
- Evaluate bladder function (PVR bladder scan)
- Document full neuro exam (strength, sensation, reflexes, saddle area)
- Inform neurosurgery immediately
2️⃣ Definitive Treatment
- 🛠 Emergency Surgical Decompression
- Lumbar laminectomy + discectomy
- Best outcomes: within 6–24 hours, ideally <12 hours
3️⃣ Adjunct Management
- Broad-spectrum IV antibiotics if epidural abscess
- Stop anticoagulants if hematoma suspected
- Corticosteroids for tumor-related compression (rare)
- Catheterization for urinary retention
📊 Key Facts (High-Yield)
- 🚨 Red flags: urinary retention + saddle anesthesia
- MRI is mandatory — do NOT rely on CT
- CES-Incomplete → better prognosis; early surgery crucial
- CES-Retention → high risk of permanent disability
- Most common cause → massive central disc herniation
- Delayed diagnosis → top malpractice claim in ED