🧠 Proteinopathies of the Central Nervous System (CNS)
Misfolded or abnormally aggregated proteins → neuronal dysfunction → progressive neurodegeneration.
Many spread in a prion-like pattern (templated misfolding + cell-to-cell propagation).
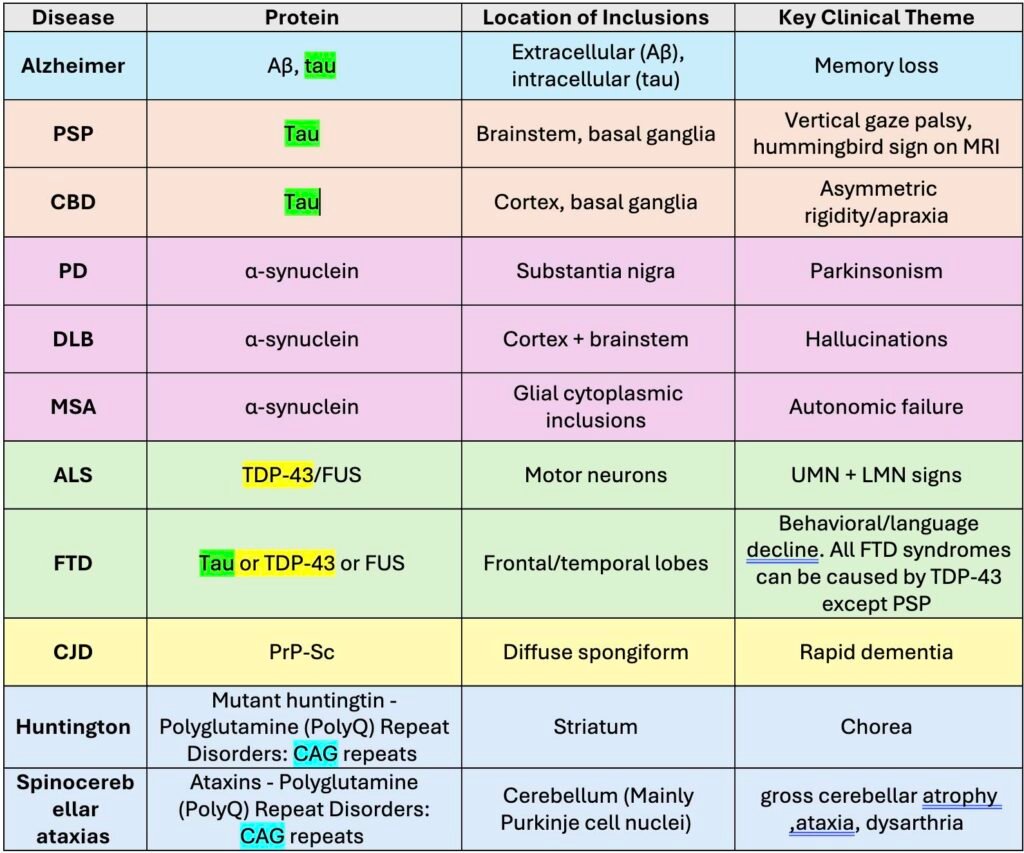
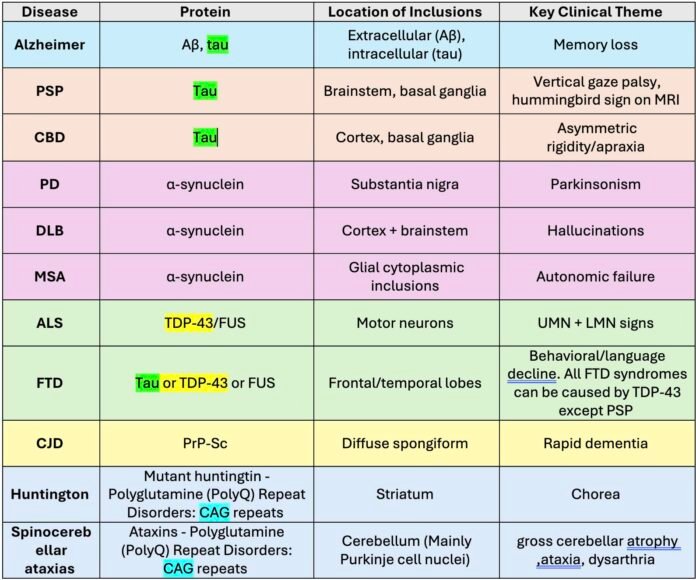
🟦 1. Alzheimer Disease (AD)
- Proteins involved:
- 🧩 Aβ plaques (extracellular)
- 🧵 Hyperphosphorylated tau tangles (intracellular)
- Key regions affected:
- Hippocampus → entorhinal cortex → widespread cortical involvement
🟨 2. Tauopathies (Non-Alzheimer)
Primary feature: intracellular accumulation of abnormal tau.
🔶 a. Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration (FTLD-tau)
- Pick disease → Pick bodies (3R tau)
- PSP → tufted astrocytes
- CBD → astrocytic plaques
- Clinical themes: behavioral change, executive dysfunction, parkinsonism, gaze palsy
🟥 3. Synucleinopathies
Core pathology: aggregation of α-synuclein.
🎯 a. Parkinson Disease (PD)
- Lewy bodies in substantia nigra
- Dopamine deficiency → bradykinesia, rigidity, resting tremor
🌙 b. Dementia With Lewy Bodies (DLB)
- Lewy bodies in cortex + brainstem
- Visual hallucinations, fluctuating cognition, REM sleep behavior disorder
⚠️ c. Multiple System Atrophy (MSA)
- Glial cytoplasmic inclusions (α-synuclein)
- Parkinsonism + autonomic failure + cerebellar signs
🟩 4. TDP-43 Proteinopathies
Protein: TDP-43 misfolding & aggregation.
🦠 a. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
- TDP-43 in motor neurons → UMN + LMN degeneration
🧩 b. FTLD-TDP
- Behavioral variant FTD or language variants
- TDP-43 inclusions in frontal & temporal lobes
🟪 5. Prion Diseases (PrP Proteinopathy)
Protein: misfolded PrP-Sc (self-replicating, infectious pattern).
Examples
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) → rapid dementia, myoclonus
- Variant CJD
- Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker (GSS)
- Fatal familial insomnia (FFI)
Hallmarks:
🧠 Spongiform change | 🔁 Templated misfolding | ⚡ Rapid progression
🟧 6. Polyglutamine (PolyQ) Repeat Disorders
Mechanism: expanded CAG repeats → toxic gain-of-function.
🎮 a. Huntington Disease
- Mutant huntingtin (expanded CAG)
- Loss in caudate + putamen
- Chorea, psychiatric symptoms, cognitive decline
🎯 b. Spinocerebellar Ataxias (SCAs)
- PolyQ-expanded ataxins → cerebellar neuron degeneration
- Cerebellar atrophy, ataxia, dysarthria
⬜ 7. Other Important Proteinopathies
⚡ a. ALS / FTD with FUS Pathology
- FUS inclusions
- Seen in TDP-43–negative ALS
🧬 b. Cerebellar Ataxia with Polyglutamine-Binding Protein-1 Inclusions
- Rare
- Linked to transcriptional dysregulation
🌀 c. Globular Glial Tauopathies
- Predominantly astrocytic & oligodendroglial tau inclusions